Tankless water heaters have become increasingly popular for homeowners around the globe. Hyper-efficient, long-lasting, and conveniently sized, tankless water heaters greatly reduce the amount of energy consumed by your household each day. However, the lifespan and performance of a tankless water heater are dramatically affected by the quality of the incoming water. Scale, a prime enemy of all appliances, can choke the heating element and prematurely destroy the unit. Sediment build-ups can clog the system and cripple the unit’s efficiency. A tankless water heater filter preserves the lifespan of your heater by guarding the unit against mineral build-up and sediment and protecting the heater from damage.
Table of Contents
What is a tankless water heater?Tankless vs tank water heatersHow much does a tankless water heater cost? Gas vs electric tankless water heatersDoes hard water harm tankless water heaters? Pros and cons of tankless water heatersDo I need a tankless water heater filter?Types of tankless water heater filtersWhat is a tankless water heater?
Tankless water heaters are also known as instantaneous water heaters because of their ability to supply hot water on demand. Because they do not store hot water in a tank, they do not use energy to constantly heat water throughout the day. Rather, they heat water when a user demands hot water. As a result, tankless water heaters are much more energy efficient than tank water heaters. This benefit gives a tankless water heater owner significant energy savings each year, and the longer lifespan of tankless heaters makes them a wise investment despite their high initial cost.
Tankless vs tank water heaters
Tankless water heaters heat water directly only when it is needed. They do not require bulky storage tanks and use far less energy than their traditional counterparts. When a hot water faucet is turned on, a sensor in the tankless water heater is alerted there is a demand for hot water. An electric heating coil or gas burner ignites, and the heat is transferred to the water circulating through the pipes in the heater. These powerful heating elements elevate the temperature of the water rapidly. The water then enters a mixing valve, where cold water is added to the water to regulate the water’s scalding temperature. Upon exiting the heater, the water passes through a second sensor. This temperature sensor reads if the water is too hot (or not hot enough) and adjusts the internal elements accordingly. The water is then distributed into the home’s plumbing and exits out of the fixture. This operation means tankless water heaters only use energy when hot water is demanded.
Traditional tank heaters use energy constantly to keep water hot and ready to use. These heaters fill 40 to 50-gallon storage tanks up with water, then drain energy keeping the water perpetually heated. Energy is dumped into keeping the stored reservoir of water hot regardless of the current demand. Furthermore, conventional tank water heaters are incredibly inconvenient. If someone washes a load of dishes right after a bath is run, you must wait for that storage tank to fill and for the water to heat up before accessing it. This can get in the way of cleaning, doing laundry, bathing, and simple household tasks. Not only do tankless water heaters reduce energy usage, but they also produce hot water on demand. With innovations in design, some recirculating tankless water heaters even produce hot water instantly.
Learn more about tank water heaters: How to fix common water heater problems
How much does a tankless water heater cost?
A tankless water heater will cost between $1,000 and $4,000, including installation. Electric tankless heaters tend to be less expensive, costing around $1,500 on average. A gas-fired tankless water heater usually costs $3,500 to install.
This is a higher price tag than storage tank water heaters, which usually range from $500 to $800 dollars to install. However, keep in mind the longevity of a tankless heater and the significant energy savings will pay for the system over time. Storage tank systems usually last about 10 years, whereas a tankless system has a lifespan of 20 years. If the tankless system saves you just $100 a year, that’s an energy savings of $2,000 over its lifetime, plus the added $800 saved where you didn’t have to replace the system ten years in. Most high-efficiency tankless water heaters will save you far more than $100 per year, especially in smaller households.
Note that these costs include the estimated installation fees of the plumber. Installing a tankless water heater is complicated electrical work and should not be attempted by a homeowner as a DIY installation. The skills of a professional licensed plumber are needed for this installation.

Gas vs electric tankless water heaters
Electric tankless heaters are cheaper, lower maintenance, and do not require extensive installation. Gas tankless heaters have significantly higher price tags than electric units, need propane or natural gas to operate, and require venting and a fresh air supply. Gas heaters will need annual maintenance inspections from licensed professionals. Since the price of natural gas is slightly cheaper than the price of electricity, the operating costs of gas heaters tend to be lower than their electric counterparts. However, gas tankless heaters do produce greenhouse gas emissions during use, and the price of natural gas tends to fluctuate. Electric tankless heaters tend to boast higher efficiency. In these units, around 98 percent of the energy used goes directly toward heating water. Conversely, gas heaters hover around 85 percent efficiency. Both units, however, are widely more efficient than tank water heaters.
Both gas and tankless heaters can claim a host of cost and energy-saving advantages compared to storage tank units. Ultimately, the choice between a gas-powered or electric tankless heater will come down to personal preference, available space, and the homeowner’s budget. In most use cases, electric tankless heaters are preferred. This is because they are cheaper, more environmentally friendly, and far easier to install. If you plan on installing multiple tankless heaters, electric units are a much more desirable choice. Since they release exhaust gases as part of the heating process, gas units require extensive venting and air circulation, a consideration you do not have to make if you are installing an electric heater. Electric tankless heaters do not release any exhaust, broadening your choice of installation locations. Gas units are also higher maintenance and far more difficult to service. Electric units are usually simple to troubleshoot and repair, which generally means they tend to have a longer lifespan than tankless gas heaters.
Does hard water harm tankless water heaters?
Hard water is water with an abundance of calcium and magnesium ions. When water passes through the layers of the earth’s crust, it absorbs calcium and magnesium from rocks like gypsum and limestone. These natural minerals create what is known as water hardness. Calcium and magnesium resist staying in a dissolute form and are eager to re-emerge as solid precipitate. This precipitate is called calcium carbonate, also known by the names limescale and scale. Scale is a crusty, white build-up that clogs pipes, leaves streaks of soap stains on glass, and is notorious for destroying appliances. Hard water is one of the most common water quality issues in the United States.
Learn more: What is hard water?
Pros and cons of tankless water heaters
Tankless water heaters provide many advantages over tank water heaters. However, there are a few negatives to be aware of before you switch to a tankless heater.
Advantages of tankless water heaters
- Energy efficient. Tankless water heaters only heat up water when there is a demand for it in the household. No energy is expended keeping water hot in between uses. These incredibly efficient units reduce water heating energy costs of the average family around 25 to 40 percent. If you install multiple tankless water heaters (targeting every hot water-using appliance) you can achieve over 50 percent reduction of energy costs. About 50% of the energy used by traditional water heaters goes toward simply maintaining the hot water’s temperature.
- Compact size. Tankless water heaters are compact units, conveniently sized to fit flush against a wall, inside a cabinet, or beneath a sink. Traditional water heaters hold 50 gallons of water. These units can use significant storage space in your garage, basement, or attic. In smaller homes, water heaters may take up space in a bathroom or hall closet. In contrast, tankless water heaters are flat and usually no longer than 2 or 3 feet. They can be installed inside or outside and, because of their size, can fit comfortably on any wall or location of your choosing.
- Increased safety. Traditional water heaters are prone to leaking, bursting, and flooding, leaving costly water damage behind. Older units are prone to leaks, a risk that is eliminated by a tankless heater, as they don’t store any water. Since tankless water heaters don’t hold any standing water in them, there’s no risk of bacteria like Legionella accumulating inside the tank and making your household sick.
- Hot water on demand. With a tankless heater, there’s no waiting around for the tank to heat your water up. If you want to step into a hot bath, you can simply turn on the hot water faucet and fill the tub up. Regardless of how much hot water was recently used, a tankless water heater provides you with hot water when you want it and where you want it. You aren’t limited by the gallon capacity of the water heater’s storage tank. Because they supply unlimited hot water, tankless systems are ideal for filling up hot tubs and whirlpools. The immediacy and convenience of a tankless water heater are some of the system’s biggest draws.
- Versatile installation options. Tankless water heaters can be installed almost anywhere you desire. You can opt for one tankless unit that heats up water for the entire household or install multiple heaters in front of every hot water-using appliance. Traditional water storage units are massive tanks that can only be installed at the home’s point of entry. This makes plumbing water filtration around the heater more difficult, as well as limits where in the house the heater can feasibly be installed. With tankless units, you have the freedom to install them wherever suits your home best.
- Longevity. Most tankless water heaters have lifespans of 20 years or longer. Though more expensive initially than conventional water heaters, tankless water heaters pay for themselves in longevity alone and last twice as long as traditional tank heaters. A typical tank heater lasts up to a decade, sometimes slightly longer. The extended lifespan of tankless units not only saves you energy costs over time, but it also saves you from costly installation and plumbing fees every ten years. Without filtration, water heater storage tanks can also fill with sediment or become clogged by scale, further reducing their expected service life.
- Wi-Fi Connectivity. One unique feature of many new tankless water heaters is Wi-Fi connectivity. These “smart tankless heaters” can remotely control the temperature of your water. If you’re getting ready to run a hot bath, you can alert your tankless heater and eliminate any waiting time. They also allow you to regulate the temperature of your heater from your phone, monitor water usage, and create a schedule for the heater to turn. If you have a recirculating tankless heater, you can use your smart heater’s app to initiate recirculation.
Disadvantages of tankless water heaters
- Initial price tag. Tankless water heaters are expensive. They cost significantly more than a storage tank-style heater system. However, because of their significant energy savings, tankless heaters will pay for themselves throughout the lifespan of the unit. Since these units are about 25 to 40 percent more efficient than storage tank heaters, tankless heaters are actually the cheaper option long term.
- Cannot operate under low flow. Tankless water heaters require a flow of at least 0.5 gallons per minute (GPM) to operate. If the flow drops below this, the water will not heat up properly. This is part of what makes a tankless water heater filter so integral to protecting the heater’s performance. If the unit is clogged with scale, or if household plumbing and appliances are scale-ridden, the flow rate will drop, and the heater will not work. By protecting the heater from sediment and hard water minerals, you can ensure your system remains efficient.
- Power dependent. Tankless water heaters rely on electrical power to work. This means if your power goes out, so does your hot water. Here, storage water heaters do have an advantage. You can still draw from the reserve of hot water after a power outage until you use up all the heated water or the water begins to cool down. A tankless system has no means of providing hot water without an electrical connection.
Do I need a tankless water heater filter?
Yes, a tankless water heater filter is essential to protecting your water heater from damage by inhibiting the accumulation of scale. Scale will clog and restrict the incoming flow rate, reduce the efficiency of the heater, and over time, cause severe damage and ultimately destroy the heater. A tankless water heater filter eliminates water-hardening minerals, preventing scale build-ups and preserving the lifespan of your heater. A tankless heater is a valuable investment. It will save you on energy costs, eliminate long waits for hot water, and last for decades if properly maintained. Letting water hardness clog the unit with scale can be detrimental and prematurely ruin your investment.
When scale forms along the heating elements within a water heater, the heater loses efficiency. When a demand for hot water is initiated, the heating elements are forced to heat up the calcified crust of scale in addition to the heating element, causing them to expend more energy than normal. A buildup of scale will make the transfer of heat within the heater much more difficult. The unit is forced to work twice as hard to achieve the optimal temperature range. This puts a significant strain on the heater. A scale-ridden tankless heater will overexert itself during operation. This will inevitably cause the unit to fail far sooner than its expected lifespan. Furthermore, this wasted energy runs counterintuitive to the motivation behind installing a tankless system to begin with. All your energy savings will be lost if the machine is coated in scale.
Tankless water heaters are particularly vulnerable against hard water. When the water is heated, the calcium and magnesium will emerge as scale much faster. Hot water aids in mineral content converting into a solid form. Tankless heaters and storage-tank water heaters alike are very likely to become choked by scale. Other hot water-using appliances, like dishwashers, laundry machines, and showerheads, are also prime targets for scale build-up if left undefended.
Learn more: How to prevent limescale buildup in your home
Types of tankless water heater filters
Tankless water heater filters remove scale-forming minerals and sediment from water. This protects the heater from damage, corrosion, and diminished efficiency. Tankless water heater filters utilize different methods to prevent scale from forming within the heater. These methods include phosphate, template-assisted crystallization, and proprietary scale control blends. An ion exchange water softener will also remove water-hardness causing minerals.
TAC (Template-Assisted Crystallization)
One of the most popular ways to stop scale from entering into a tankless water heater is by using a template-assisted crystallization filter inline ahead of the filter. Template-assisted crystallization (also called TAC) prevents calcium and magnesium minerals from emerging from the water and creating scale. TAC filters use tiny polymer beads covered in craters called “nucleation sites”. When the hard water flows over these beads, the calcium and magnesium ions deposit on these nucleation sites. As the nucleation sites continue to collect mineral ions, they form micro-crystals out of calcium and magnesium.
These crystals will eventually break off and flow through the heater. However, these micro-crystals are entirely stable. They will not stick to pipes or cause scale to accumulate on appliances or on heating elements. In fact, these micro-crystals help clear pre-existing scale formations out of your plumbing. TAC is the technology used in many whole-house salt-free water conditioners (or sometimes deceptively marketed as “salt-free water softeners”.) While they do not soften the water, they do render the hardness minerals incapable of emerging from solution to create scale. They are also popularly sold in cartridge form to be installed directly in front of tankless water heaters.
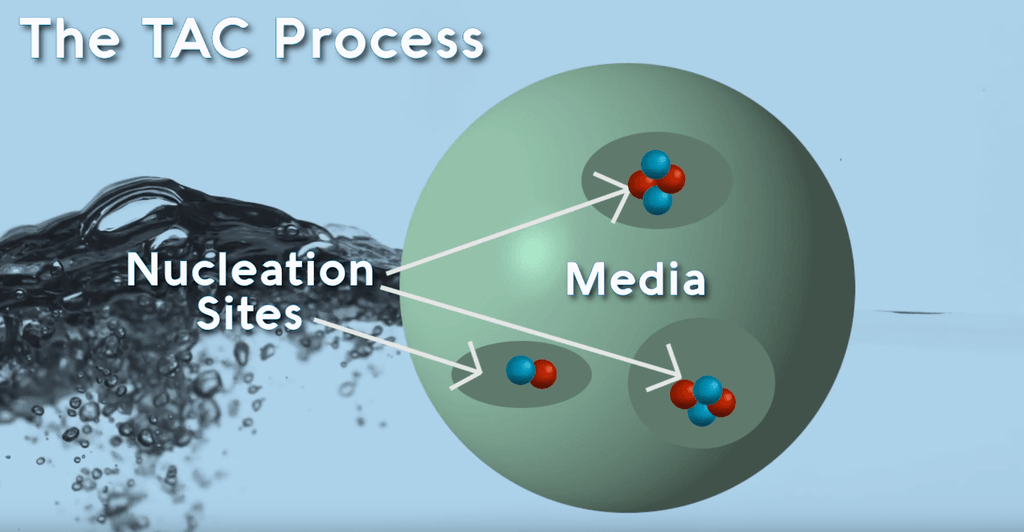
TAC media can continue to isolate hardness ions and create micro-crystals for 3 to 5 years before needing to be replaced. However, it is vital to note that the TAC beads are sensitive to chlorine. Chlorine is used by most municipal water suppliers as a water disinfectant, eliminating waterborne pathogenic bacteria. However, the chlorine will wear down the TAC media prematurely. Chlorine monopolizes the nucleation sites, preventing micro-crystals from forming. While most city water will not have exorbitant levels of chlorine, it is recommended that all TAC filters are preceded by a carbon filter. The carbon filter will adsorb the chlorine content, which will improve both the efficiency of the TAC filter as well as the taste of your water.
Learn more: Water conditioners vs water softeners | The truth about salt-free water softeners
Phosphate filters
One of the properties of phosphate crystals (polyphosphates) is an ability to inhibit the crystallization of magnesium and calcium. Because of this trait, phosphate filters are known as “scale inhibitors”. When the water flows through the filter, the phosphates attach to the calcium and magnesium ions. These “sequestered” water hardness minerals are unable to emerge out of the water, obstructing the formation of scale.
Phosphate cartridges are depleted over time. The speed at which they deplete depends on the severity of hardness in the water they treat. The harder the water, the more phosphate will be used to isolate and neutralize the hardness minerals. Most phosphate cartridges last between six months and one year. However, phosphate filters are generally not the first choice for a tankless water heater filter. Hot water causes phosphates to break apart, dramatically reducing their efficacy as an anti-scale agent. If you plan to use a phosphate scale inhibitor, make sure it is installed on a cold water line to see the greatest results. If hot water passes through the filter, the heat will break down the phosphate before the phosphate can sequester it. This allows calcium and magnesium to enter the tankless heater and form scale.
Water softeners
If you have hard water, one of the best and most time-honored solutions is a water softener. A water softener will protect not only your tankless water heater from scale, but ensure your entire home is free from hard water damage. Your dishwasher, your laundry machine, and all your hot water fixtures can fall victim to the scourge of hard water if it is not properly addressed. Hard water also prevents soap from lathering, dries out hair and skin, and causes streaks to form on your shower doors and kitchen countertops. If you are concerned about preserving your tankless heater, it is worth investing in a water treatment system that will protect your whole home.
Water softeners are whole house water filtration systems that eliminate water hardness entirely. Phosphates and TAC both neutralize water hardness minerals and stop them from becoming scale. Only a water softener altogether removes the minerals from the water. Water softeners eliminate water hardness by passing hard water through a bed of polystyrene resin beads. These beads are flushed with a salt-rich brine solution, which leaves each resin bead charged with a sodium ion. When hard water passes through the column of resin beads, a process called ion exchange occurs. The calcium and magnesium ions are attracted to the positive charge of the resin beads. The beads then grab ahold of the mineral ions and release sodium ions into the water. The water then exits the tank and flows into your home softened and mineral free. When the resin beads have taken on enough mineral ions, a regeneration cycle is initiated. This flushes the resin, sending the hardness ions to the drain and recharging the beads with sodium ions.
Water softeners are a fantastic way to preserve not only the lifespan and performance of your tankless water heater, but they are also a worthwhile investment for anyone living in a region with hard water. Softeners protect your heater from being choked with scale, as well as eliminate the myriad of headaches that water hardness brings to a home.
Learn more: How water softeners work | 5 benefits of having a water softener
Sediment filters
A sediment filter is another valuable tankless water heater pre-filter. Tankless water heaters have a narrow inlet designed exclusively for water flow. Dirt, debris, and particulate matter can all result in the unit clogging. If sediment builds up in a tankless heater, the unit will malfunction and eventually stop working altogether. Depending on the extent of the damage, you will need to purchase replacement parts or potentially an entirely new unit.
Tank-style water heaters are better equipped to handle sediment. Sediment will accumulate in the tank and settle at the bottom. The tank is then periodically flushed, clearing the tank of sediment. Waiting too long to flush a storage tank water heater will eventually result in leaks and diminished efficiency. However, tankless heaters have no place to store the sediment. Any internal blockage on a tankless heater will result in immediate damage to the system and a significant reduction in efficiency. If the inlet valve becomes obstructed by sediment, water will be unable to even enter the system, much less fill your tub with hot water.
If your home relies on well water, you are the most vulnerable to sediment build-ups. Everything from sand to flecks of dirt to solid debris can make its way into your water. While sediment filters do not reduce heavy metals or mitigate scale, they will ensure the passageway to your tankless heater remains open. Installing a whole-house spin-down sediment filter or a 5-micron pre-filter before your tankless water heater will keep it clean from debris and preserve the unit’s efficiency.
Learn more: How sediment filters work | How spin-down filters work
If you have any additional questions, please do not hesitate to contact us.

Can i change the inlet water filter (I’m using glycol) with a larger one and connect it to the outgoing hot glycol or incoming piping system?